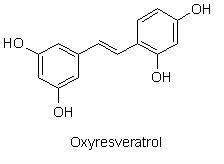
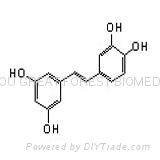
Resveratrol (3,4’,5-trihydroxy-trans-stilbene) is a phytoalexin found mainly in the skin of grapes and red wine, and demonstrates anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular protective, and cancer chemopreventive properties. In vitro and in vivo, Resveratrol is extensively metabolized to several glucuronides and sulfates. Resveratrol undergoes cytochrome P450 catalyzed hydroxylation to piceantannol, 3,4,4’,5-tetrahydroxy-trans-stilbene, and to two other unidentified mono- and dihydroxyresveratrol analogues. As Piceatannol demonstrates a several fold higher antileukaemic activity than resveratrol and as COX-2 is a known target for anticancer activity. Piceatannol and other Resveratrol analogues might achieve a better and more selective COX-2 inhibition than Resveratrol, such as Pterostilbene, Oxyresveratrol, Rhapontigenin, Isorhapontigenin, et al.
In view of the market of Resveratrol, its analogs have potential broad market prospects.